SipMiddlewareApi » History » Revision 165
« Previous |
Revision 165/238
(diff)
| Next »
Tijmen de Mes, 04/19/2012 05:01 PM
Middleware API¶
This chapter describes the Middleware API for SIP SIMPLE client SDK that can be used for developing a user interface (e.g. Graphical User Interface). The Middleware provides a non-blocking API that communicates with the user interface asynchronously by using Notifications. For its configuration, the Middleware uses the Configuration API.
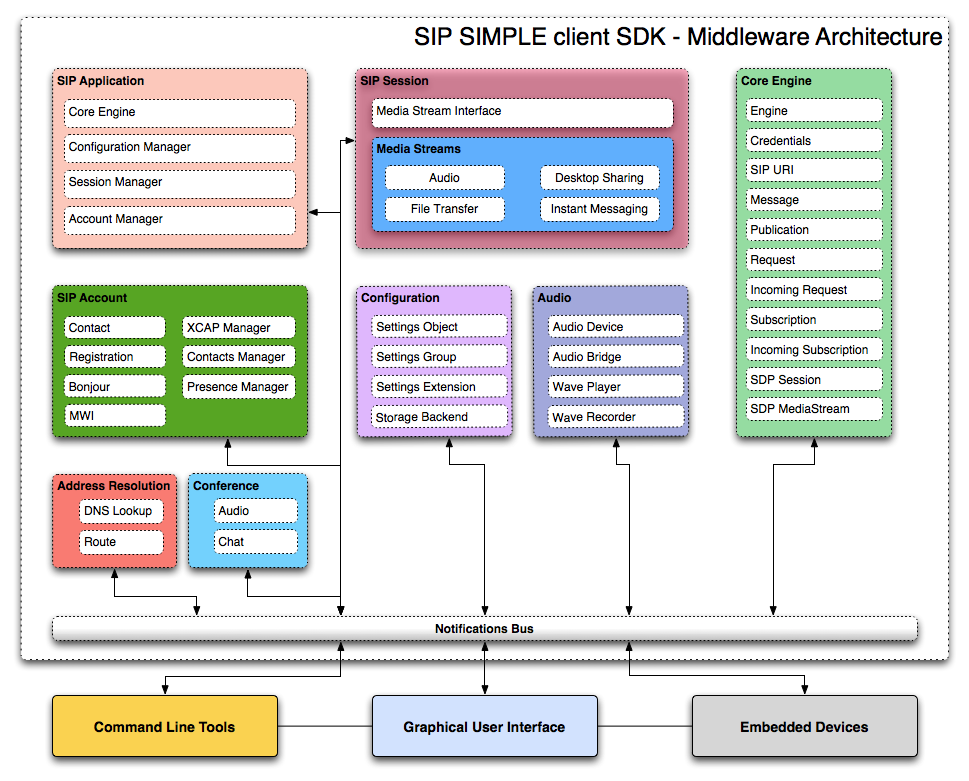
SIPApplication¶
Implemented in [browser:sipsimple/application.py]
Implements a high-level application responsable for starting and stopping various sub-systems required to implement a fully featured SIP User Agent application. The SIPApplication class is a Singleton and can be instantiated from any part of the code, obtaining a reference to the same object. The SIPApplication takes care of initializing the following components:- the twisted thread
- the configuration system, via the ConfigurationManager
- the core Engine using the settings in the configuration
- the AccountManager, using the accounts in the configuration
- the SessionManager, in order to handle incoming sessions
- two AudioBridges, using the settings in the configuration
The attributes in this class can be set and accessed on both this class and its subclasses, as they are implemented using descriptors which keep single value for each attribute, irrespective of the class from which that attribute is set/accessed. Usually, all attributes should be considered read-only.
methods¶
__init__(self)
Instantiates a new SIPApplication.
start(self, storage)
Starts the
SIPApplicationwhich initializes all the components in the correct order. Thestorageis saved as an attribute which other entities like theConfiguration Managerwill use to take the appropriate backend. If any error occurs with loading the configuration, the exception raised by theConfigurationManageris propagated by this method andSIPApplicationcan be started again. After this, any fatal errors will result in the SIPApplication being stopped and unusable, which means the whole application will need to stop. This method returns as soon as the twisted thread has been started, which means the application must wait for theSIPApplicationDidStartnotification in order to know that the application started.
stop(self)
Stop all the components started by the SIPApplication. This method returns immediately, but a
SIPApplicationDidEndnotification is sent when all the components have been stopped.
attributes¶
running
Trueif the SIPApplication is running (it has been started and it has not been told to stop),Falseotherwise.
storage
Holds an object which implements the
ISIPSimpleStorageinterface which will be used to provide a storage facility to other middleware components.
local_nat_type
String containing the detected local NAT type.
alert_audio_mixer
The
AudioMixerobject created on the alert audio device as defined by the configuration (by SIPSimpleSettings.audio.alert_device).
alert_audio_bridge
An
AudioBridgewhereIAudioPortobjects can be added to playback sound to the alert device.
alert_audio_device
An
AudioDevicewhich corresponds to the alert device as defined by the configuration. This will always be part of the alert_audio_bridge.
voice_audio_mixer
The
AudioMixerobject created on the voice audio device as defined by the configuration (by SIPSimpleSettings.audio.input_device and SIPSimpleSettings.audio.output_device).
voice_audio_bridge
An
AudioBridgewhereIAudioPortobjects can be added to playback sound to the output device or record sound from the input device.
voice_audio_device
An
AudioDevicewhich corresponds to the voice device as defined by the configuration. This will always be part of the voice_audio_bridge.
notifications¶
SIPApplicationWillStart
This notification is sent just after the configuration has been loaded and the twisted thread started, but before any other components have been initialized.
timestamp:
A
datetime.datetimeobject indicating when the notification was sent.
SIPApplicationDidStart
This notification is sent when all the components have been initialized. Note: it doesn't mean that all components have succeeded, for example, the account might not have registered by this time, but the registration process will have started.
timestamp:
A
datetime.datetimeobject indicating when the notification was sent.
SIPApplicationWillEnd
This notification is sent as soon as the
stop()method has been called.
timestamp:
A
datetime.datetimeobject indicating when the notification was sent.
SIPApplicationDidEnd
This notification is sent when all the components have been stopped. All components have been given reasonable time to shutdown gracefully, such as the account unregistering. However, because of factors outside the control of the middleware, such as network problems, some components might not have actually shutdown gracefully; this is needed because otherwise the SIPApplication could hang indefinitely (for example because the system is no longer connected to a network and it cannot be determined when it will be again).
timestamp:
A
datetime.datetimeobject indicating when the notification was sent.
SIPApplicationFailedToStartTLS
This notification is sent when a problem arises with initializing the TLS transport. In this case, the Engine will be started without TLS support and this notification contains the error which identifies the cause for not being able to start the TLS transport.
timestamp:
A
datetime.datetimeobject indicating when the notification was sent.
error:
The exception raised by the Engine which identifies the cause for not being able to start the TLS transport.
Storage API¶
Different middleware components may need to store data, i.e. configuration files or XCAP documents. The Storage API defines a collection of backends which other components will use to store their data.
API Definition¶
The Storage API currently requires the following attributes to be defined as per the ISIPSimpleStorage interface:
configuration_backend
The backend used for storing the configuration.
xcap_storage_factory
Factory used to create XCAP storage backends for each account.
Provided implementations¶
Two storage implementations are provided: FileStorage and MemoryStorage both located in the sipsimple.storage module.
SIP Sessions¶
SIP sessions are supported by the sipsimple.session.Session class and independent stream classes, which need to implement the sipsimple.streams.IMediaStream interface. The Session class takes care of the signalling, while the streams offer the actual media support which is negotiated by the Session. The streams which are implemented in the SIP SIMPLE middleware are provided in modules within the sipsimple.streams package, but they are accessible for import directly from sipsimple.streams. Currently, the middleware implements two types of streams, one for RTP data, with a concrete implementation in the AudioStream class, and one for MSRP sessions, with concrete implementations in the ChatStream, FileTransferStream and DesktopSharingStream classes. However, the application can provide its own stream implementation, provided they respect the IMediaStream interface.
The sipsimple.streams module also provides a mechanism for automatically registering media streams in order for them to be used for incoming sessions. This is explained in more detail in MediaStreamRegistry.
SessionManager¶
Implemented in [browser:sipsimple/session.py]
The sipsimple.session.SessionManager class is a singleton, which acts as the central aggregation point for sessions within the middleware.
Although it is mainly used internally, the application can use it to query information about all active sessions.
The SessionManager is implemented as a singleton, meaning that only one instance of this class exists within the middleware. The SessionManager is started by the SIPApplication and takes care of handling incoming sessions and closing all sessions when SIPApplication is stopped.
attributes¶
sessions
A property providing a copy of the list of all active
Sesssionobjects within the application, meaning anySessionobject that exists globally within the application and is not in theNULLorTERMINATEDstate.
methods¶
__init__(self)
Instantiate a new
SessionManagerobject.
start(self)
Start the
SessionManagerin order to be able to handle incoming sessions. This method is called automatically when SIPApplication is started. The application should not call this method directly.
stop(self)
End all connected sessions. This method is called automatically when SIPApplication is stopped. The application should not call this method directly.
Session¶
Implemented in [browser:sipsimple/session.py]
A sipsimple.session.Session object represents a complete SIP session between the local and a remote endpoints. Both incoming and outgoing sessions are represented by this class.
A Session instance is a stateful object, meaning that it has a state attribute and that the lifetime of the session traverses different states, from session creation to termination. State changes are triggered by methods called on the object by the application or by received network events. These states and their transitions are represented in the following diagram:
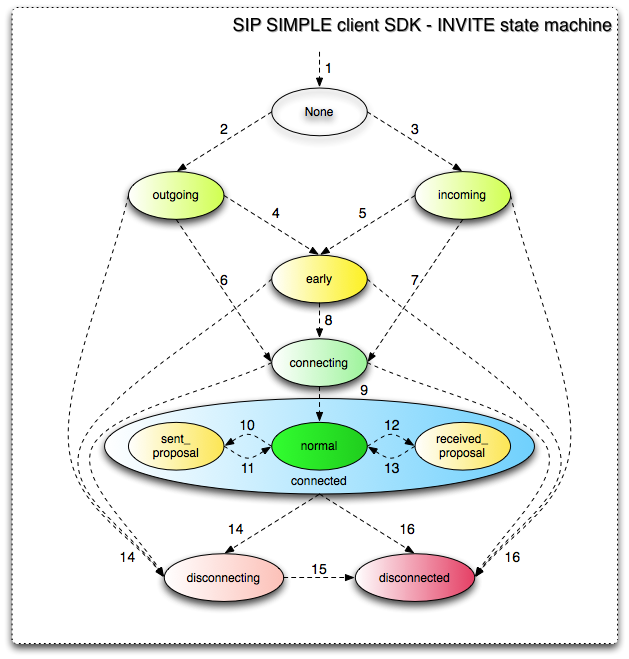
Although these states are crucial to the correct operation of the Session object, an application using this object does not need to keep track of these states, as a set of notifications is also emitted, which provide all the necessary information to the application.
The Session is completely independent of the streams it contains, which need to be implementations of the sipsimple.streams.IMediaStream interface. This interface provides the API by which the Session communicates with the streams. This API should not be used by the application, unless it also provides stream implementations or a SIP INVITE session implementation.
methods¶
__init__(self, account)
Creates a new
Sessionobject in theNonestate.
account:
The local account to be associated with this
Session.
connect(self, to_header, routes, streams, is_focus=False, subject=None)
Will set up the
Sessionas outbound and propose the new session to the specified remote party and move the state machine to theoutgoingstate.
Before contacting the remote party, aSIPSessionNewOutgoingnotification will be emitted.
If there is a failure or the remote party rejected the offer, aSIPSessionDidFailnotification will be sent.
Any time a ringing indication is received from the remote party, aSIPSessionGotRingIndicationnotification is sent.
If the remote party accepted the session, aSIPSessionWillStartnotification will be sent, followed by aSIPSessionDidStartnotification when the session is actually established.
This method may only be called while in theNonestate.
to_header:
A
sipsimple.core.ToHeaderobject representing the remote identity to initiate the session to.
routes:
An iterable of
sipsimple.util.Routeobjects, specifying the IP, port and transport to the outbound proxy.
These routes will be tried in order, until one of them succeeds.
streams:
A list of stream objects which will be offered to the remote endpoint.
is_focus:
Boolean flag indicating if the
isfocusparameter should be added to theContactheader according to RFC 4579.
subject:
Session subject. If not None a
Subjectheader will be added with the specified value.
send_ring_indication(self)
Sends a 180 provisional response in the case of an incoming session.
accept(self, streams)
Calling this methods will accept an incoming session and move the state machine to the
acceptingstate.
When there is a new incoming session, aSIPSessionNewIncomingnotification is sent, after which the application can call this method on the sender of the notification.
After this method is called,SIPSessionWillStartfollowed bySIPSessionDidStartwill be emitted, orSIPSessionDidFailon an error.
This method may only be called while in theincomingstate.
streams:
A list of streams which needs to be a subset of the proposed streams which indicates which streams are to be accepted. All the other proposed streams will be rejected.
reject(self, code=603, reason=None)
Reject an incoming session and move it to the
terminatingstate, which eventually leads to theterminatedstate.
Calling this method will cause theSessionobject to emit aSIPSessionDidFailnotification once the session has been rejected.
This method may only be called while in theincomingstate.
code:
An integer which represents the SIP status code in the response which is to be sent. Usually, this is either 486 (Busy) or 603 (Decline/Busy Everywhere).
reason:
The string which is to be sent as the SIP status reason in the response, or None if PJSIP's default reason for the specified code is to be sent.
accept_proposal(self, streams)
When the remote party proposes to add some new streams, signaled by the
SIPSessionGotProposalnotification, the application can use this method to accept the stream(s) being proposed.
After calling this method aSIPSessionGotAcceptProposalnotification is sent, unless an error occurs while setting up the new stream, in which case aSIPSessionHadProposalFailurenotification is sent and a rejection is sent to the remote party. As with any action which causes the streams in the session to change, aSIPSessionDidRenegotiateStreamsnotification is also sent.
This method may only be called while in thereceived_proposalstate.
streams:
A list of streams which needs to be a subset of the proposed streams which indicates which streams are to be accepted. All the other proposed streams will be rejected.
reject_proposal(self, code=488, reason=None)
When the remote party proposes new streams that the application does not want to accept, this method can be used to reject the proposal, after which a
SIPSessionGotRejectProposalorSIPSessionHadProposalFailurenotification is sent.
This method may only be called while in thereceived_proposalstate.
code:
An integer which represents the SIP status code in the response which is to be sent. Usually, this is 488 (Not Acceptable Here).
reason:
The string which is to be sent as the SIP status reason in the response, or None if PJSIP's default reason for the specified code is to be sent.
add_stream(self, stream)
Proposes a new stream to the remote party.
Calling this method will cause aSIPSessionGotProposalnotification to be emitted.
After this, the state machine will move into thesending_proposalstate until either aSIPSessionGotAcceptProposal,SIPSessionGotRejectProposalorSIPSessionHadProposalFailurenotification is sent, informing the application if the remote party accepted the proposal. As with any action which causes the streams in the session to change, aSIPSessionDidRenegotiateStreamsnotification is also sent.
This method may only be called while in theconnectedstate.
remove_stream(self, stream)
Stop the stream and remove it from the session, informing the remote party of this. Although technically this is also done via an SDP negotiation which may fail, the stream will always get remove (if the remote party refuses the re-INVITE, the result will be that the remote party will have a different view of the active streams than the local party).
This method may only be called while in theconnectedstate.
cancel_proposal(self)
This method cancels a proposal of adding a stream to the session by sending a CANCEL request. A
SIPSessionGotRejectProposalnotification will be sent with code 487.
hold(self)
Put the streams of the session which support the notion of hold on hold.
This will cause aSIPSessionDidChangeHoldStatenotification to be sent.
This method may be called in any state and will send the re-INVITE as soon as it is possible.
unhold(self)
Take the streams of the session which support the notion of hold out of hold.
This will cause aSIPSessionDidChangeHoldStatenotification to be sent.
This method may be called in any state and will send teh re-INVITE as soon as it is possible.
end(self)
This method may be called any time after the
Sessionhas started in order to terminate the session by sending a BYE request.
Right before termination aSIPSessionWillEndnotification is sent, after terminationSIPSessionDidEndis sent.
transfer(self, target_uri, replaced_session=None)
Proposes a blind call transfer to a new target URI or assisted transfer to an URI belonging to an already established session.
accept_transfer(self)
Accepts an incoming call transfer request.
reject_transfer(self, code=486, *reason_=None)
Rejects an incoming call transfer request.
attributes¶
state
The state the object is currently in, being one of the states from the diagram above.
account
The
sipsimple.account.Accountorsipsimple.account.BonjourAccountobject that theSessionis associated with.
On an outbound session, this is the account the application specified on object instantiation.
direction
A string indicating the direction of the initial negotiation of the session.
This can be eitherNone, "incoming" or "outgoing".
transport
A string representing the transport this
Sessionis using:"udp","tcp"or"tls".
start_time
The time the session started as a
datetime.datetimeobject, orNoneif the session was not yet started.
stop_time
The time the session stopped as a
datetime.datetimeobject, orNoneif the session has not yet terminated.
on_hold
Boolean indicating whether the session was put on hold, either by the local or the remote party.
remote_user_agent
A string indicating the remote user agent, if it provided one.
Initially this will beNone, it will be set as soon as this information is received from the remote party (which may be never).
local_identity
The
sipsimple.core.FrozenFromHeaderorsipsimple.core.FrozenToHeaderidentifying the local party, if the session is active,Noneotherwise.
remote_identity
The
sipsimple.core.FrozenFromHeaderorsipsimple.core.FrozenToHeaderidentifying the remote party, if the session is active,Noneotherwise.
streams
A list of the currently active streams in the
Session.
proposed_streams
A list of the currently proposed streams in the
Session, orNoneif there is no proposal in progress.
conference
A
ConferenceHandlerobject instance (or Null). It can be later used to add/remove participants from a remote conference.
subject
The session subject as a unicode object.
replaced_session
A
Sessionobject instance (or Null). It can be used for assisted call transfer.
transfer_handler
A
TransferHandlerobject instance (or Null). It is used for managing the call transfer process.
transfer_info
A
TransferInfoobject instance (or Null). It is used for describing the details of a call transfer operation.
notifications¶
SIPSessionNewIncoming
Will be sent when a new incoming
Sessionis received.
The application should listen for this notification to get informed of incoming sessions.
timestamp:
A
datetime.datetimeobject indicating when the notification was sent.
streams:
A list of streams that were proposed by the remote party.
SIPSessionNewOutgoing
Will be sent when the application requests a new outgoing
Session.
timestamp:
A
datetime.datetimeobject indicating when the notification was sent.
streams:
A list of streams that were proposed to the remote party.
SIPSessionGotRingIndication
Will be sent when an outgoing
Sessionreceives an indication that a remote device is ringing.
timestamp:
A
datetime.datetimeobject indicating when the notification was sent.
SIPSessionGotProvisionalResponse
Will be sent whenever the
Sessionreceives a provisional response as a result of sending a (re-)INVITE.
timestamp:
A
datetime.datetimeobject indicating when the notification was sent.
code:
The SIP status code received.
reason:
The SIP status reason received.
SIPSessionWillStart
Will be sent just before a
Sessioncompletes negotiation.
In terms of SIP, this is sent after the final response to theINVITE, but before theACK.
timestamp:
A
datetime.datetimeobject indicating when the notification was sent.
SIPSessionDidStart
Will be sent when a
Sessioncompletes negotiation and all the streams have started.
In terms of SIP this is sent after theACKwas sent or received.
timestamp:
A
datetime.datetimeobject indicating when the notification was sent.
streams:
The list of streams which now form the active streams of the
Session.
SIPSessionDidFail
This notification is sent whenever the session fails before it starts.
The failure reason is included in the data attributes.
This notification is never followed bySIPSessionDidEnd.
timestamp:
A
datetime.datetimeobject indicating when the notification was sent.
originator:
A string indicating the originator of the
Session. This will either be "local" or "remote".
code:
The SIP error code of the failure.
reason:
A SIP status reason.
failure_reason:
A string which represents the reason for the failure, such as
"user_request","missing ACK","SIP core error...".
SIPSessionWillEnd
Will be sent just before terminating a
Session.
timestamp:
A
datetime.datetimeobject indicating when the notification was sent.
SIPSessionDidEnd
Will be sent always when a
Sessionends as a result of remote or local session termination.
timestamp:
A
datetime.datetimeobject indicating when the notification was sent.
originator:
A string indicating who originated the termination. This will either be "local" or "remote".
end_reason:
A string representing the termination reason, such as
"user_request","SIP core error...".
SIPSessionDidChangeHoldState
Will be sent when the session got put on hold or removed from hold, either by the local or the remote party.
timestamp:
A
datetime.datetimeobject indicating when the notification was sent.
originator:
A string indicating who originated the hold request, and consequently in which direction the session got put on hold.
on_hold:
Trueif there is at least one stream which is on hold andFalseotherwise.
partial:
Trueif there is at least one stream which is on hold and one stream which supports hold but is not on hold andFalseotherwise.
SIPSessionGotProposal
Will be sent when either the local or the remote party proposes to add streams to the session.
timestamp:
A
datetime.datetimeobject indicating when the notification was sent.
originator:
The party that initiated the stream proposal, can be either "local" or "remote".
streams:
A list of streams that were proposed.
SIPSessionGotRejectProposal
Will be sent when either the local or the remote party rejects a proposal to have streams added to the session.
timestamp:
A
datetime.datetimeobject indicating when the notification was sent.
originator:
The party that initiated the stream proposal, can be either "local" or "remote".
code:
The code with which the proposal was rejected.
reason:
The reason for rejecting the stream proposal.
streams:
The list of streams which were rejected.
SIPSessionGotAcceptProposal
Will be sent when either the local or the remote party accepts a proposal to have stream( added to the session.
timestamp:
A
datetime.datetimeobject indicating when the notification was sent.
originator:
The party that initiated the stream proposal, can be either "local" or "remote".
streams:
The list of streams which were accepted.
proposed_streams:
The list of streams which were originally proposed.
SIPSessionHadProposalFailure
Will be sent when a re-INVITE fails because of an internal reason (such as a stream not being able to start).
timestamp:
A
datetime.datetimeobject indicating when the notification was sent.
failure_reason:
The error which caused the proposal to fail.
streams:
The streams which were part of this proposal.
SIPSessionDidRenegotiateStreams
Will be sent when a media stream is either activated or deactivated.
An application should listen to this notification in order to know when a media stream can be used.
timestamp:
A
datetime.datetimeobject indicating when the notification was sent.
action:
A string which is either
"add"or"remove"which specifies what happened to the streams the notificaton referes to
streams:
A list with the streams which were added or removed.
SIPSessionDidProcessTransaction
Will be sent whenever a SIP transaction is complete in order to provide low-level details of the progress of the INVITE dialog.
timestamp:
Adatetime.datetimeobject indicating when the notification was sent.
originator:
The initiator of the transaction,
"local"or"remote".
method:
The method of the request.
code:
The SIP status code of the response.
reason:
The SIP status reason of the response.
ack_received:
This attribute is only present for INVITE transactions and has one of the values
True,Falseor"unknown". The last value may occur then PJSIP does not let us know whether the ACK was received or not.
SIPSessionTransferNewOutgoing
Will be sent whenever a SIP session initiates an outgoing call transfer request.
timestamp:
A
datetime.datetimeobject indicating when the notification was sent.
transfer_destination:
The destination SIP URI of the call transfer request.
transfer_source:
The source SIP URI of the call transfer request.
SIPSessionTransferDidStart
Will be sent whenever a call transfer has been started.
timestamp:
A
datetime.datetimeobject indicating when the notification was sent.
SIPSessionTransferDidFail
Will be sent whenever a call transfer request has failed.
timestamp:
A
datetime.datetimeobject indicating when the notification was sent.
code:
The SIP failure code reported by the SIP stack.
reason:
The reason of the failure as a string.
As an example for how to use the Session object, the following provides a basic Python program that initiates an outgoing SIP session request see Minimalist Session Example code.
Updated by Tijmen de Mes almost 14 years ago · 165 revisions